Each person must complete TWO or THREE of the following, and print the summary at the end. Each table needs to divide up the quizzes so that there will be at least two samples of each per table. Doing these quizzes should take you about 15 minutes.
Carbon #1
Carbon #2
Carbon #3
Carbon #4
Now, we need to find out about the Carbon cycle. Print off one copy of each of the following documents and bring back to your table. Read and share the information with one another, underlining the top facts in the article (underline no more than 5 sentences). As a table, highlight with a yellow marker anything your group decides is an OPINION, and not supported by evidence.
Article 1
Article 2
Article 3
Article 4
Article 5
Article 6
Take a look at your group's carbon footprint data, and personally decide the FIVE most important things that you can do at this point to reduce your carbon footprint. Each person should make a poster that has these FIVE things listed, as well as graphics to support your choices.
Hand in the group readings and the posters at the end of the hour. Paperclip the material for each table.
Questions: Tweet me, please!
Monday, September 28, 2009
Friday, September 25, 2009
Tuesday, September 22, 2009
Vocabulary review on Alternative Energy QUIZ MOVED TO THURSDAY
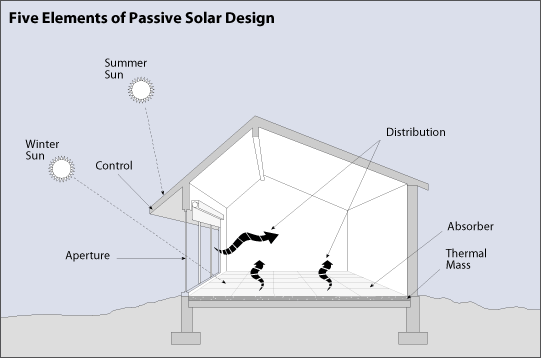
Passive Solar: using solar energy with thermal mass to heat housing without extra mechanical devices
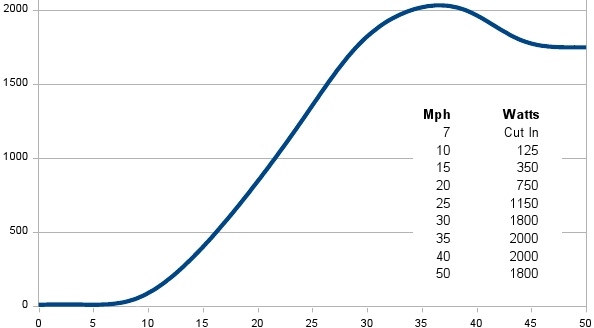
 Wind Energy: Harnessing the power of convective heat transfer to power a device to create electricity or energy
Wind Energy: Harnessing the power of convective heat transfer to power a device to create electricity or energyInsulation: Materials designed to prevent heat loss.
Turbine: A device that is designed to convert energy from one form to another.
Furling: The down slope of a curve when the windmill no longer functions as well as it should because the speed is too great.
 Thermal mass: materials designed to warm up from the sun's radiation, and then to cool into the air when the sun is not present
Thermal mass: materials designed to warm up from the sun's radiation, and then to cool into the air when the sun is not present  Multiple Pane Windows: Windows that protect against heat loss because of an air space between the glass layers.
Multiple Pane Windows: Windows that protect against heat loss because of an air space between the glass layers.Annual Cost factor: the amount of money saved by using appropriate insulation. Click here
Alternative Energy: Any type of energy that does not take fossil fuels, and minimizes the impact on the environment
Monday, September 21, 2009
You Decide

Your parents, impressed with your new-found knowledge in the area of alternative energy, want to know which technology would be best for your home and your budget.
1. Based on your classroom knowledge, define passive solar, active solar, and wind energy. Draw a sketch to accompany each definition.
2. Draw a sketch of your home, noting where the windows are in relationship to N, S, E, or W.
3. List three pieces of evidence for the technology you choose. This is based on work done in class.
4. Find the cost of the technology you choose. This is based on Internet research. At least 3 URLs must be listed, along with the cost at each website.
Finally, check out EcoGeek to find two additional pieces of evidence that support your idea. Make certain you reference the title of the blog post, or the URL where you found the information.
This is due on MONDAY, 9/28, at the beginning of class.
Solar Ovens: passive solar technology
Your goal is to design, with ONE partner, the best solar cooker for here in Iowa. You may modify one of the following designs:
Pizza box cooker
Open Box cooker
CD cooker
Pringles can cooker
Pop bottle cooker
Remember, these designs are only starting points. You can add insulation, reflective foil, or black paint to make things better. You will have 60 minutes in class on Tuesday to design these. Ovens are due at the start of class on Thursday. You will heat a) a thermometer and b) a marshmallow OR b) water to test their effectiveness.
Tuesday, September 15, 2009
Solar Cars--Active solar cell technology
Please answer the following questions on the blog:
1. What were the problems with using solar cells alone to power a vehicle?
2. Why does gear ratio matter?
3. How do angles affect the performance of your vehicle? Specifically, what angles are you talking about?
4. Which do you believe to be more effective alternative energy: active solar or passive solar? Why?
1. What were the problems with using solar cells alone to power a vehicle?
2. Why does gear ratio matter?
3. How do angles affect the performance of your vehicle? Specifically, what angles are you talking about?
4. Which do you believe to be more effective alternative energy: active solar or passive solar? Why?
Monday, September 14, 2009
Group Wind Notes
Here is the compilation of everything you came up with about WIND ENERGY
Pros
- Great source of energy
- Saves fossil fuels
- Little noise
- Modern wind turbines are far less harmful to wildlife
- Saves money
- Creates jobs
- Natural Resource
- Doesn’t emit harmful emissions
- Clean energy
- “Green”
- Can be used day or night
- Receive significant federal subsidies
- Used for pumping water, grinding grain, sawing, and pushing a sailboat
Cons
- Costs a lot of money
- Needs a large amount of wind
- Takes lots of space
- Kills birds
- Drag of blades
- Few people know much about wind energy
- Turbines are huge
- Vulnerable to weather
- No power plant is reliable 100% of the time
Design
- Short in the blades
- Flat towards middle
- Small number of blades
- Lighter materials
- Thin blades
- Angle of blades
- Smooth surface
- Blades are smaller at end for less drag
- 50-90 meters tall
- 3 blades
- Efficient blades
- Want less drag
- 2 basic designs- vertical – egg beater or horizontal axis
- Backed up by a generator
- Small tip
- Tower is made of steel
- Blades are made of fiberglass with polyester or wood epoxy
Other
- Shorten blades
- Changing the pitch
- Less blades
- Lighter materials
- Smooth surfaces
- Wildlife problems
Energy Effect
- Power many houses
- Saves many needed resources
- Lowers energy cost
- No air or water pollution
- No greenhouse gases
- 1 turbine could supply 1400 houses in 1 hour
- 100% reliable
- Wind energy is converted form of solar energy
- Fed into electric power lines and delivered to customers
- 1 megawatt of wind
- Transforms kinetic energy of the wind into mechanical or electrical energy harnessed for practical use
- Wind energy requires production tax credit (ptc) to achieve economics
- Wind energy is unpredictable
- Wind energy is more expensive than conventional energy
Equipment Problems
- Creates drag if not made right
- Time consuming to make blades
- Build up of junk on the blades
- If something breaks someone would have to go up high to fix it
- Long time to fix them
- Very expensive
- More power than electricity
Friday, September 11, 2009
Thursday, September 10, 2009
Friday, September 4, 2009
FRIDAY ASSIGNMENT
I had a family emergency overnight, so I will not be in. Ask PT if you want more information. Here is your assignment.
Step 1: Answer the blog post on SPF using your gmail account. If it doesn't work, handwrite it and hand in.
Step 2: Use a scissors and carefully cut southern windows and eastern windows on your shoe box house.
Step 3: Place a wall that is 1 to 2 cm thick into place using manila folders and the insulation you brought. Tape is on the file cabinet....
Step 4. Make Double Pane Windows by placing Saran Wrap over the window openings.
Step 5: Place a thermometer inside your house so you can track the temperature through the window wrap. *Hint: The lid should open and shut, for easy access.
Step 6: Place a heat lamp 80 cm away from your house, as shown in the diagram Track the warming rate for 5 minutes and then the cooling rate for 5 minutes.
Congratulate yourself, and keep those houses on top of the cabinets on the east wall. Put your names on them. We will be using them next week!
Step 1: Answer the blog post on SPF using your gmail account. If it doesn't work, handwrite it and hand in.
Step 2: Use a scissors and carefully cut southern windows and eastern windows on your shoe box house.
Step 3: Place a wall that is 1 to 2 cm thick into place using manila folders and the insulation you brought. Tape is on the file cabinet....
Step 4. Make Double Pane Windows by placing Saran Wrap over the window openings.
Step 5: Place a thermometer inside your house so you can track the temperature through the window wrap. *Hint: The lid should open and shut, for easy access.
Step 6: Place a heat lamp 80 cm away from your house, as shown in the diagram Track the warming rate for 5 minutes and then the cooling rate for 5 minutes.
Congratulate yourself, and keep those houses on top of the cabinets on the east wall. Put your names on them. We will be using them next week!
Thursday, September 3, 2009
SPF Protection lab
Based on what we did yesterday, what do you think is the purpose of SPF suncreen? What mistaken ideas (misconceptions) might people have about sunscreen effectiveness? What did you observe in your lab that might help change their minds?
Wednesday, September 2, 2009
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)